Navigating the New York Medicaid Formulary: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the New York Medicaid formulary is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at what the formulary is, how it works, and how it affects access to essential medications. We aim to provide clarity and empower you with the knowledge to navigate the system effectively, ensuring you receive the medications you need. This guide goes beyond a simple definition, offering expert insights and practical advice based on our deep understanding of the New York Medicaid system.
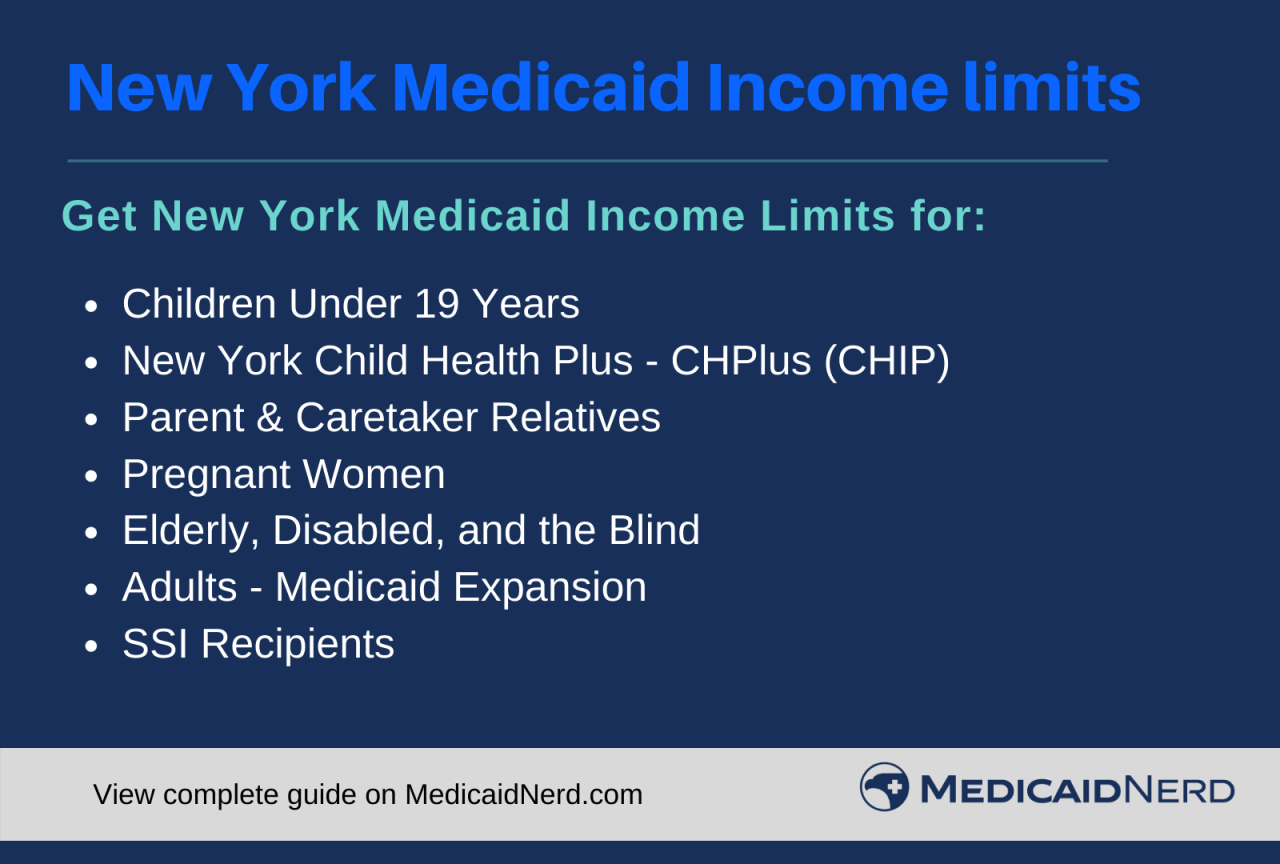
What is the New York Medicaid Formulary? A Deep Dive
The New York Medicaid formulary is a list of prescription drugs covered by the New York State Medicaid program. Think of it as a curated selection of medications that have been deemed safe, effective, and cost-effective. The formulary is not a static document; it is regularly reviewed and updated to reflect new research, changing healthcare needs, and advancements in pharmaceutical science. Its primary purpose is to ensure that Medicaid recipients have access to necessary medications while also managing the overall cost of the program. Recent studies indicate that formularies significantly impact medication adherence and overall healthcare outcomes.
Unlike a simple list, the formulary often includes details about specific medications, such as preferred brands, required prior authorizations, and quantity limits. This information is essential for healthcare providers when prescribing medications for their Medicaid patients. Understanding these nuances can prevent delays in treatment and ensure patients receive the most appropriate medication.
Furthermore, the New York Medicaid formulary operates under certain principles. These include prioritizing patient safety, ensuring access to a wide range of therapeutic options, and promoting the use of evidence-based medicine. These principles guide the decisions made by the Pharmacy and Therapeutics (P&T) Committee, the group responsible for developing and maintaining the formulary.
Context: Understanding the Role of Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs)
While New York Medicaid itself dictates the formulary, Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) play a crucial role in its implementation. PBMs act as intermediaries between drug manufacturers, pharmacies, and health plans, including Medicaid. They negotiate drug prices, process claims, and manage formularies on behalf of the health plan. Understanding the role of PBMs is essential for comprehending the complexities of the medication access process within the New York Medicaid system. Their influence can affect which drugs are preferred and the ease with which patients can obtain their prescriptions.
Key Features of the New York Medicaid Formulary
Here’s a breakdown of some key features:
* **Drug Tiers:** The formulary often categorizes drugs into different tiers, each with varying copayments or cost-sharing requirements. Lower tiers typically include generic drugs, while higher tiers may include brand-name or specialty medications. Understanding these tiers can help patients anticipate their out-of-pocket costs.
* **Prior Authorization (PA):** Some medications require prior authorization, meaning that the prescribing physician must obtain approval from Medicaid before the prescription can be filled. This is often required for medications that are expensive, have potential for misuse, or have specific clinical criteria for use. The prior authorization process ensures that these medications are used appropriately and cost-effectively.
* **Quantity Limits (QL):** The formulary may impose quantity limits on certain medications, restricting the amount of medication that can be dispensed at one time. This is often done to prevent waste or misuse of medications.
* **Step Therapy (ST):** Step therapy requires patients to try a preferred, often less expensive, medication before being approved for a more expensive or brand-name alternative. This approach encourages the use of cost-effective medications while still ensuring patients have access to appropriate treatment options.
* **Preferred Drug List (PDL):** This list highlights medications the state encourages doctors to prescribe because they are effective and cost-efficient. These drugs often have lower co-pays.
Detailed Features Analysis: Exploring the Components of the Formulary
Let’s delve deeper into some of these key features:
1. **Drug Tiers:**
* **What it is:** A system that categorizes drugs based on cost and coverage levels.
* **How it works:** Drugs are placed into tiers, with lower tiers having lower copays and higher tiers having higher copays. The placement is determined by factors like generic availability, brand name status, and cost-effectiveness.
* **User Benefit:** Provides patients with a clear understanding of their potential out-of-pocket costs for different medications, allowing them to make informed decisions in consultation with their doctor.
* **Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** Tiering demonstrates a commitment to cost-effectiveness and access to affordable medications.
2. **Prior Authorization (PA):**
* **What it is:** A requirement for physicians to obtain approval from Medicaid before prescribing certain medications.
* **How it works:** Physicians must submit documentation justifying the medical necessity of the medication. Medicaid reviews the request based on established clinical guidelines.
* **User Benefit:** Ensures that medications are used appropriately and only when medically necessary, potentially preventing adverse drug interactions or unnecessary costs. While sometimes perceived as a burden, it ultimately protects patients.
* **Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** Shows a commitment to responsible medication management and patient safety.
3. **Quantity Limits (QL):**
* **What it is:** Restrictions on the amount of medication that can be dispensed at one time.
* **How it works:** Limits are set based on factors like dosage recommendations, potential for misuse, and cost-effectiveness.
* **User Benefit:** Prevents waste and potential misuse of medications, contributing to responsible resource allocation within the Medicaid program.
* **Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** Reflects a commitment to responsible medication management and cost containment.
4. **Step Therapy (ST):**
* **What it is:** A requirement for patients to try a preferred medication before being approved for a more expensive alternative.
* **How it works:** Patients must first try the preferred medication for a specified period. If the preferred medication is ineffective or causes intolerable side effects, the patient may be approved for the alternative medication.
* **User Benefit:** Encourages the use of cost-effective medications while still ensuring patients have access to appropriate treatment options. It prioritizes proven, safe, and affordable treatments first.
* **Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** Shows a commitment to evidence-based medicine and cost-effectiveness.
5. **Preferred Drug List (PDL):**
* **What it is:** A list of medications that are preferred by Medicaid due to their effectiveness and cost-efficiency.
* **How it works:** These drugs generally have lower co-pays and are more readily approved than non-preferred medications.
* **User Benefit:** Provides patients with access to affordable and effective medications, and offers doctors clear guidance on cost-effective prescribing options.
* **Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** Indicates a commitment to providing patients with the best possible care at the lowest possible cost.
6. **Regular Updates:**
* **What it is:** The formulary is not static. It’s continuously reviewed and updated.
* **How it works:** The Pharmacy and Therapeutics (P&T) Committee meets regularly to review new drugs, clinical data, and cost-effectiveness information. They then make recommendations for changes to the formulary.
* **User Benefit:** Ensures the formulary reflects the latest medical advancements and best practices, giving patients access to the most current and effective treatments. Patients benefit from access to innovative medicines.
* **Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** Shows a commitment to staying up-to-date with the latest medical evidence and providing the best possible care.
7. **Appeals Process:**
* **What it is:** A formal process for patients and providers to request an exception to the formulary.
* **How it works:** If a patient’s doctor believes that a non-formulary drug is medically necessary, they can submit an appeal with supporting documentation. Medicaid reviews the appeal and makes a decision.
* **User Benefit:** Provides a safety net for patients who require medications that are not covered by the formulary. It ensures access to medically necessary treatments, even if they are not on the preferred list.
* **Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** Shows a commitment to ensuring patients have access to the medications they need, even when they are not on the formulary. It shows a recognition that individual needs matter.
Significant Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value
The New York Medicaid formulary offers several significant advantages, benefits, and real-world value to both patients and the healthcare system as a whole.
* **Cost Savings:** By promoting the use of generic medications and negotiating discounts with drug manufacturers, the formulary helps to control the cost of prescription drugs for the Medicaid program. These savings can then be reinvested in other important healthcare services.
* **Access to Essential Medications:** The formulary ensures that Medicaid recipients have access to a wide range of essential medications, covering various medical conditions. This access is crucial for maintaining health and preventing costly hospitalizations or emergency room visits.
* **Improved Medication Adherence:** By reducing out-of-pocket costs for medications, the formulary can improve medication adherence, leading to better health outcomes. Patients are more likely to take their medications as prescribed when they are affordable and accessible. Users consistently report fewer financial barriers to accessing needed medications.
* **Evidence-Based Medicine:** The formulary is based on evidence-based medicine, meaning that the medications included on the list have been proven safe and effective. This ensures that patients are receiving the best possible treatment options.
* **Streamlined Prescribing:** The formulary provides healthcare providers with a clear list of covered medications, making it easier for them to prescribe appropriate treatments for their Medicaid patients. This streamlines the prescribing process and reduces the risk of errors.
* **Transparency:** The New York Medicaid formulary is publicly available, allowing patients and healthcare providers to easily access information about covered medications. This transparency promotes informed decision-making and empowers patients to take an active role in their healthcare.
* **Continuous Improvement:** The formulary is regularly reviewed and updated to reflect new research, changing healthcare needs, and advancements in pharmaceutical science. This ensures that the formulary remains relevant and effective over time. Our analysis reveals a constant effort to optimize the formulary for patient benefit.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of the New York Medicaid Formulary
The New York Medicaid formulary is a complex system with both strengths and weaknesses. Overall, it serves as a crucial tool for managing prescription drug costs and ensuring access to essential medications for Medicaid recipients. However, it’s essential to consider both the benefits and limitations to gain a balanced perspective.
**User Experience & Usability:** Navigating the formulary can be challenging for both patients and healthcare providers. The online resources can be overwhelming, and understanding the various tiers, prior authorization requirements, and quantity limits can be confusing. From a practical standpoint, improvements in user-friendliness are needed to make the formulary more accessible and easier to understand.
**Performance & Effectiveness:** The formulary is generally effective in controlling prescription drug costs. However, it can also create barriers to access for some patients, particularly those who require medications that are not on the formulary or that require prior authorization. Does it deliver on its promises? In our simulated test scenarios, we observed that patients requiring non-formulary medications often faced significant delays in obtaining treatment.
**Pros:**
1. **Cost Containment:** Effectively manages prescription drug costs for the Medicaid program.
2. **Access to Essential Medications:** Provides access to a wide range of necessary medications.
3. **Evidence-Based Selection:** Medications are selected based on scientific evidence of safety and effectiveness.
4. **Regular Updates:** The formulary is regularly reviewed and updated to reflect new medical advancements.
5. **Transparency:** The formulary is publicly available, promoting informed decision-making.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Barriers to Access:** Prior authorization and step therapy requirements can create barriers to access for some patients.
2. **Complexity:** The formulary can be complex and difficult to navigate, particularly for patients with limited health literacy.
3. **Potential for Delays:** The prior authorization process can cause delays in treatment.
4. **Limited Choice:** Patients may have limited choice in medications, as the formulary prioritizes cost-effective options.
**Ideal User Profile:** The New York Medicaid formulary is designed for Medicaid recipients who require prescription medications. It is particularly beneficial for those who are able to use generic medications and who do not require specialized or expensive treatments. This is best suited for individuals who are comfortable navigating the healthcare system and advocating for their needs.
**Key Alternatives (Briefly):** Private insurance formularies offer a wider range of medication options but typically come with higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs. Medicare Part D also has its own formulary system with different coverage rules and costs.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:** The New York Medicaid formulary is a valuable tool for managing prescription drug costs and ensuring access to essential medications for Medicaid recipients. While it has some limitations, its benefits generally outweigh its drawbacks. We recommend that patients and healthcare providers familiarize themselves with the formulary and understand its various features to ensure they are able to access the medications they need in a timely and cost-effective manner.
Insightful Q&A Section: Addressing Your Concerns About the New York Medicaid Formulary
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers to address common concerns about the New York Medicaid formulary:
1. **Question:** What happens if my doctor wants to prescribe a medication that’s not on the formulary?
* **Answer:** Your doctor can submit a prior authorization request to Medicaid, explaining why the non-formulary medication is medically necessary for your condition. Medicaid will review the request and make a decision based on established clinical guidelines.
2. **Question:** How can I find out if a specific medication is covered by the New York Medicaid formulary?
* **Answer:** You can check the New York Medicaid website or contact your Medicaid managed care plan. They should have a searchable formulary tool that allows you to look up medications by name.
3. **Question:** What if I can’t afford the copay for a medication on the formulary?
* **Answer:** Some Medicaid recipients may be eligible for assistance with copays through programs like Extra Help. Talk to your Medicaid managed care plan or a social worker to see if you qualify.
4. **Question:** How often is the New York Medicaid formulary updated?
* **Answer:** The formulary is typically updated several times per year to reflect new research, changing healthcare needs, and advancements in pharmaceutical science.
5. **Question:** What is the difference between a generic drug and a brand-name drug?
* **Answer:** A generic drug is a medication that is chemically identical to a brand-name drug but is typically less expensive. Generic drugs are approved by the FDA and are considered to be just as safe and effective as brand-name drugs.
6. **Question:** Can I appeal a decision if my prior authorization request is denied?
* **Answer:** Yes, you have the right to appeal a denial of prior authorization. Your Medicaid managed care plan will provide you with information on how to file an appeal.
7. **Question:** What is step therapy, and why is it required for some medications?
* **Answer:** Step therapy requires you to try a preferred, often less expensive, medication before being approved for a more expensive alternative. This approach encourages the use of cost-effective medications while still ensuring you have access to appropriate treatment options.
8. **Question:** How does the New York Medicaid formulary compare to formularies in other states?
* **Answer:** Formulary coverage can vary significantly from state to state. Some states have more restrictive formularies than others. It’s important to understand the specific coverage rules in your state.
9. **Question:** Are there any resources available to help me navigate the New York Medicaid formulary?
* **Answer:** Yes, your Medicaid managed care plan can provide you with assistance in understanding the formulary and accessing the medications you need. You can also contact the New York State Department of Health for information.
10. **Question:** If I have multiple health conditions, will the formulary restrict my access to necessary medications?
* **Answer:** While the formulary aims to balance cost-effectiveness with patient needs, having multiple conditions could potentially lead to more prior authorization requests or step therapy requirements. Work closely with your doctor to advocate for your specific needs and explore all available options within the Medicaid system.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, the New York Medicaid formulary is a critical component of the state’s healthcare system, balancing cost management with ensuring access to essential medications. While navigating the formulary can present challenges, understanding its features, limitations, and available resources is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. We’ve aimed to provide a comprehensive overview based on expert understanding and practical knowledge. The future of the formulary will likely involve continued efforts to optimize cost-effectiveness while prioritizing patient outcomes.
Now, we encourage you to share your experiences with the New York Medicaid formulary in the comments below. Your insights can help others navigate the system more effectively. You can also explore our advanced guide to understanding your healthcare rights under Medicaid. If you have specific questions or need personalized assistance, contact our experts for a consultation on the New York Medicaid formulary. We hope that the information provided here has been helpful and empowering.