Gooey Stool: A Comprehensive Guide to Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions
Gooey stool. The very phrase can evoke a sense of unease and uncertainty. If you’ve experienced this change in your bowel movements, you’re likely searching for answers: What does it mean? What’s causing it? And, most importantly, what can you do about it? This comprehensive guide aims to provide you with expert insights into the causes, symptoms, and potential solutions for gooey stool, empowering you to understand your digestive health and take proactive steps towards well-being. We’ll delve into the underlying mechanisms, explore various contributing factors, and offer evidence-based strategies for managing and resolving this common digestive concern. Our goal is to deliver a trustworthy resource, reflecting our deep understanding and experience in digestive health matters.
Understanding Gooey Stool: Definition, Characteristics, and Scope
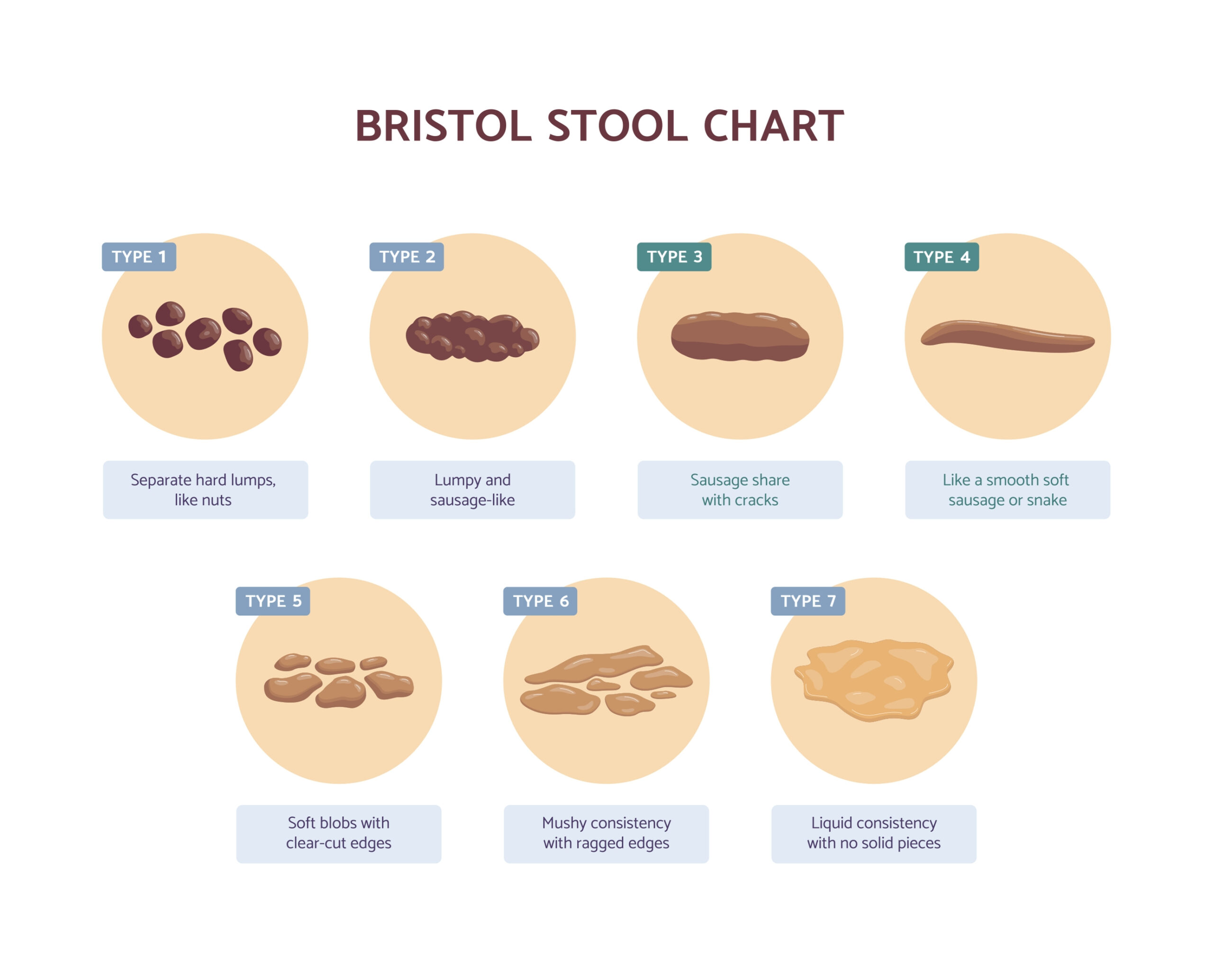
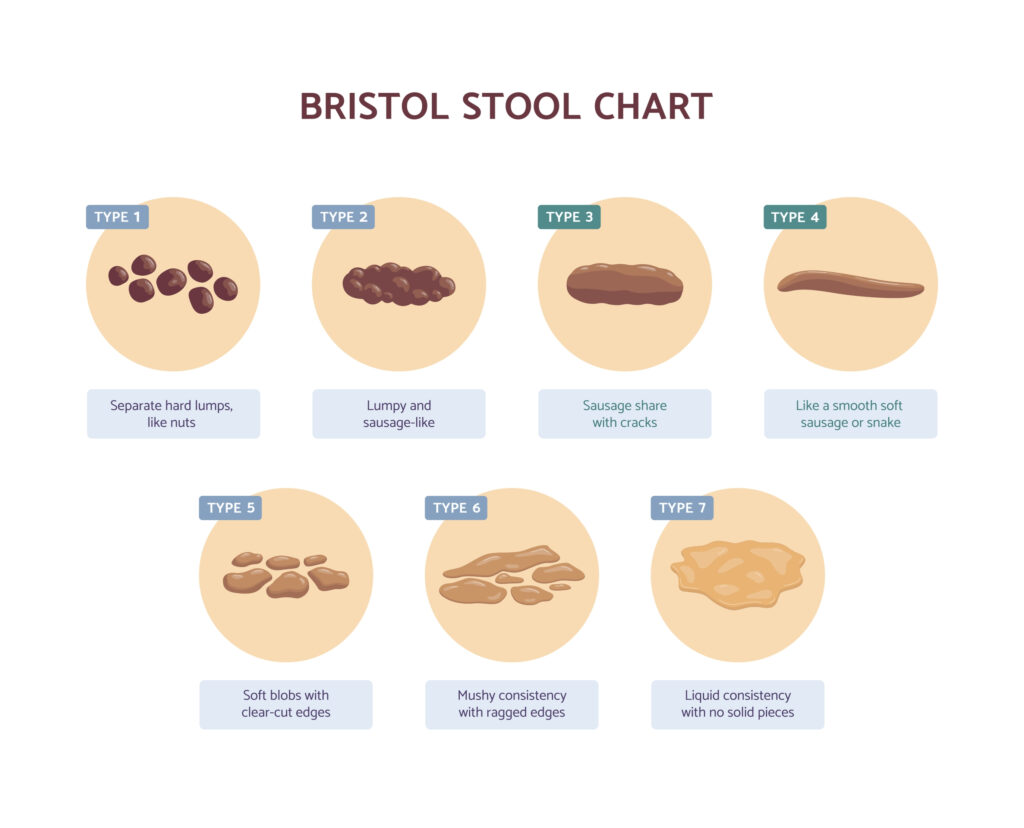
What exactly constitutes “gooey stool”? It’s more than just a subjective feeling; it refers to stool that has an abnormally soft, sticky, and often mucus-laden consistency. This differs from normal stool, which is typically formed and easily passed. Gooey stool often sticks to the toilet bowl and may be difficult to flush. The consistency can range from slightly softer than usual to almost liquid, and the color may vary depending on the underlying cause. Recognizing these characteristics is the first step in identifying a potential problem.
The scope of gooey stool can be quite broad, ranging from a temporary, isolated occurrence to a chronic, recurring issue. It can be a symptom of various underlying conditions, from minor dietary indiscretions to more serious gastrointestinal disorders. Therefore, a thorough evaluation is crucial to determine the root cause and implement appropriate management strategies.
Distinguishing Gooey Stool from Other Stool Consistencies
It’s important to differentiate gooey stool from other types of abnormal stool. Diarrhea, for example, is characterized by frequent, loose, and watery stools, while constipation involves infrequent and difficult bowel movements with hard, dry stools. Gooey stool, on the other hand, presents with a unique combination of softness, stickiness, and often the presence of mucus. Black or tarry stools typically indicate bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract, while pale or clay-colored stools may suggest a problem with bile production or flow. Understanding these distinctions is vital for accurate self-assessment and communication with your healthcare provider.
The Role of Mucus in Gooey Stool
Mucus is a naturally occurring substance that lines the intestinal tract, providing lubrication and protection. A small amount of mucus in stool is normal. However, an excessive amount of mucus, particularly when accompanied by a gooey consistency, can be a sign of inflammation or irritation in the digestive system. Conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and infections can all lead to increased mucus production and gooey stool.
Potential Causes of Gooey Stool: A Deep Dive into Contributing Factors
Numerous factors can contribute to the development of gooey stool. These can be broadly categorized into dietary factors, infections, medications, and underlying medical conditions. Identifying the potential cause is crucial for effective management.
Dietary Factors and Gooey Stool
What you eat plays a significant role in the consistency of your stool. Certain foods can increase mucus production or alter the balance of gut bacteria, leading to gooey stool. Common culprits include:
* **High-fat foods:** Fatty foods can be difficult to digest and may lead to increased mucus secretion.
* **Dairy products:** Lactose intolerance or sensitivity to dairy proteins can cause inflammation and gooey stool.
* **Artificial sweeteners:** Some artificial sweeteners, such as sorbitol and xylitol, can have a laxative effect and contribute to loose, gooey stools.
* **Spicy foods:** Spicy foods can irritate the digestive tract and increase mucus production.
* **Excessive fiber intake:** While fiber is generally beneficial for digestive health, excessive intake, particularly of insoluble fiber, can sometimes lead to loose stools.
Infections and Gooey Stool
Bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections can disrupt the normal functioning of the digestive system and cause gooey stool. Common infectious agents include:
* **Bacteria:** *Salmonella*, *Campylobacter*, and *E. coli* are common bacterial causes of gastroenteritis, which can manifest as gooey stool.
* **Viruses:** Norovirus and rotavirus are frequent viral culprits, particularly in children.
* **Parasites:** *Giardia* and *Cryptosporidium* are parasitic infections that can cause chronic diarrhea and gooey stool.
Medications and Gooey Stool
Certain medications can have side effects that affect stool consistency. These include:
* **Antibiotics:** Antibiotics can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, leading to diarrhea and gooey stool.
* **Laxatives:** Overuse of laxatives can cause loose, watery stools and may contribute to a gooey consistency.
* **Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs):** NSAIDs can irritate the lining of the stomach and intestines, potentially leading to increased mucus production and gooey stool.
Underlying Medical Conditions and Gooey Stool
In some cases, gooey stool can be a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as:
* **Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS):** IBS is a common functional gastrointestinal disorder that can cause a variety of symptoms, including abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits, including gooey stool.
* **Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD):** IBD, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, is characterized by chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, which can lead to gooey stool, abdominal pain, and bloody stools.
* **Celiac disease:** Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten, which can damage the small intestine and cause various digestive symptoms, including gooey stool.
* **Malabsorption syndromes:** Conditions that interfere with the absorption of nutrients, such as pancreatic insufficiency or short bowel syndrome, can lead to abnormal stool consistency.
Expert Solutions: Managing and Treating Gooey Stool
The approach to managing gooey stool depends on the underlying cause. In many cases, simple dietary and lifestyle changes can provide relief. However, if the problem persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, medical evaluation and treatment may be necessary.
Dietary and Lifestyle Modifications
* **Identify and eliminate trigger foods:** Keep a food diary to track your diet and identify any foods that seem to worsen your symptoms. Common trigger foods include dairy, fatty foods, artificial sweeteners, and spicy foods.
* **Increase fiber intake gradually:** If you suspect that your fiber intake is too low, increase it gradually to avoid digestive upset. Focus on soluble fiber sources, such as oats, beans, and fruits.
* **Stay hydrated:** Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help soften stools and prevent constipation.
* **Probiotics:** Consider taking a probiotic supplement to help restore the balance of gut bacteria. Choose a probiotic that contains multiple strains of beneficial bacteria.
* **Manage stress:** Stress can exacerbate digestive symptoms. Practice relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Medical Evaluation and Treatment
If dietary and lifestyle changes don’t provide relief, or if you experience any of the following symptoms, seek medical attention:
* **Persistent gooey stool for more than a few days**
* **Bloody stools**
* **Severe abdominal pain**
* **Fever**
* **Unexplained weight loss**
Your doctor may recommend various tests to determine the underlying cause of your gooey stool, such as:
* **Stool tests:** To check for infections, parasites, or inflammation.
* **Blood tests:** To look for signs of inflammation or infection.
* **Colonoscopy:** To examine the colon for abnormalities, such as polyps or inflammation.
* **Upper endoscopy:** To examine the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum for abnormalities.
Treatment will depend on the underlying cause. For example, infections may require antibiotics or antiparasitic medications. Inflammatory bowel disease may require anti-inflammatory medications or immunosuppressants. Celiac disease requires a strict gluten-free diet.
The Role of Digestive Enzymes in Managing Gooey Stool
Digestive enzymes play a crucial role in breaking down food into smaller, absorbable molecules. A deficiency in digestive enzymes can lead to malabsorption and digestive symptoms such as bloating, gas, and gooey stool. Supplementing with digestive enzymes can help improve digestion and reduce these symptoms.
Understanding Digestive Enzyme Function
Different digestive enzymes break down different types of food:
* **Amylase:** Breaks down carbohydrates into simple sugars.
* **Protease:** Breaks down proteins into amino acids.
* **Lipase:** Breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
* **Lactase:** Breaks down lactose (milk sugar) into glucose and galactose.
Benefits of Digestive Enzyme Supplementation
Digestive enzyme supplements can be beneficial for individuals with:
* **Pancreatic insufficiency:** A condition in which the pancreas does not produce enough digestive enzymes.
* **Lactose intolerance:** A condition in which the body cannot digest lactose.
* **Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS):** Digestive enzymes can help improve digestion and reduce symptoms such as bloating and gas.
* **Age-related enzyme decline:** Enzyme production naturally declines with age.
Choosing the Right Digestive Enzyme Supplement
When choosing a digestive enzyme supplement, consider the following factors:
* **Enzyme types:** Choose a supplement that contains a broad spectrum of enzymes to help break down all types of food.
* **Potency:** Look for a supplement with a high potency of each enzyme.
* **Source:** Digestive enzymes can be derived from animal, plant, or microbial sources. Choose a source that aligns with your dietary preferences.
* **Third-party testing:** Look for a supplement that has been third-party tested for purity and potency.
Probiotics: A Powerful Tool for Gut Health and Stool Consistency
Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host. They can help restore the balance of gut bacteria, improve digestion, and reduce symptoms such as bloating, gas, and gooey stool.
How Probiotics Work
Probiotics exert their beneficial effects through various mechanisms, including:
* **Competing with harmful bacteria:** Probiotics can compete with harmful bacteria for nutrients and binding sites in the gut, preventing them from colonizing and causing infection.
* **Producing antimicrobial substances:** Some probiotics produce substances that kill or inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria.
* **Strengthening the gut barrier:** Probiotics can help strengthen the gut barrier, preventing harmful substances from entering the bloodstream.
* **Modulating the immune system:** Probiotics can help regulate the immune system, reducing inflammation and improving immune function.
Choosing the Right Probiotic Supplement
When choosing a probiotic supplement, consider the following factors:
* **Strain diversity:** Choose a supplement that contains multiple strains of beneficial bacteria. Different strains have different effects on the gut.
* **CFU count:** Look for a supplement with a high CFU (colony forming unit) count. This indicates the number of live bacteria in each dose.
* **Delivery system:** Some probiotics are formulated with a special delivery system to protect the bacteria from stomach acid and ensure that they reach the intestines alive.
* **Storage:** Some probiotics require refrigeration to maintain their potency. Check the storage instructions on the label.
Comprehensive Review of Digestive Health Solutions
While we cannot endorse specific brands, we can offer a general review of the types of products available to help manage gooey stool. This section focuses on providing an unbiased assessment of the categories of products available, emphasizing user experience, performance, and effectiveness.
Enzyme Supplements
* **User Experience & Usability:** Enzyme supplements are generally easy to use, typically taken before meals. Some may come in capsule form, while others are chewable.
* **Performance & Effectiveness:** The effectiveness of enzyme supplements depends on the underlying cause of the digestive issues. For those with enzyme deficiencies, they can be highly effective in improving digestion and reducing symptoms.
* **Pros:** Can significantly improve digestion, reduce bloating and gas, and improve nutrient absorption.
* **Cons:** May not be effective for all causes of digestive issues, some individuals may experience side effects such as nausea or diarrhea, and quality can vary between brands.
* **Ideal User Profile:** Individuals with diagnosed enzyme deficiencies, those experiencing bloating and gas after meals, and those with IBS.
Probiotic Supplements
* **User Experience & Usability:** Probiotic supplements are also easy to use, typically taken daily. They come in various forms, including capsules, powders, and liquids.
* **Performance & Effectiveness:** Probiotics can be effective in restoring the balance of gut bacteria, improving digestion, and reducing symptoms such as bloating and gas. The effectiveness depends on the strain and the individual’s gut microbiome.
* **Pros:** Can improve gut health, boost the immune system, and reduce symptoms of IBS and other digestive disorders.
* **Cons:** May cause mild side effects such as gas or bloating initially, and the effectiveness can vary depending on the individual and the strain of probiotic.
* **Ideal User Profile:** Individuals with gut imbalances, those recovering from antibiotic use, and those with IBS.
Dietary Fiber Supplements
* **User Experience & Usability:** Fiber supplements are typically taken daily, mixed with water or juice. Some may have a gritty texture or a strong flavor.
* **Performance & Effectiveness:** Fiber supplements can help regulate bowel movements, improve stool consistency, and promote satiety. The effectiveness depends on the type of fiber and the individual’s digestive system.
* **Pros:** Can improve bowel regularity, lower cholesterol levels, and promote weight management.
* **Cons:** May cause bloating and gas if introduced too quickly, and some individuals may find the taste or texture unpleasant.
* **Ideal User Profile:** Individuals with constipation, those looking to increase their fiber intake, and those looking to manage their weight.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are some frequently asked questions about gooey stool:
**Q1: Is it normal to have gooey stool occasionally?**
**A:** Occasional gooey stool can be normal, especially after dietary changes or mild digestive upset. However, persistent or frequent gooey stool warrants further investigation.
**Q2: Can stress cause gooey stool?**
**A:** Yes, stress can significantly impact digestive function and contribute to changes in stool consistency, including gooey stool. Managing stress is crucial for overall digestive health.
**Q3: What does it mean if my gooey stool is also pale in color?**
**A:** Pale or clay-colored gooey stool may indicate a problem with bile production or flow. Bile is responsible for giving stool its normal brown color. This warrants prompt medical attention.
**Q4: Can food allergies cause gooey stool?**
**A:** Yes, food allergies or sensitivities can trigger inflammation in the digestive tract, leading to increased mucus production and gooey stool. Identifying and eliminating trigger foods is essential.
**Q5: How long should I wait before seeing a doctor about gooey stool?**
**A:** If your gooey stool persists for more than a few days, is accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as blood, fever, or severe abdominal pain, or if you have a history of digestive disorders, you should see a doctor promptly.
**Q6: Are there any home remedies for gooey stool?**
**A:** Dietary modifications, such as avoiding trigger foods and staying hydrated, can often help alleviate mild cases of gooey stool. Probiotics and digestive enzymes may also be beneficial. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for persistent or severe cases.
**Q7: Can medications cause gooey stool even if I’ve been taking them for a long time?**
**A:** Yes, some medications can cause digestive side effects, including gooey stool, even after prolonged use. If you suspect a medication is causing your symptoms, discuss it with your doctor.
**Q8: Is gooey stool always a sign of a serious medical condition?**
**A:** No, gooey stool is not always a sign of a serious medical condition. It can often be caused by dietary factors, stress, or mild infections. However, it’s important to rule out any underlying medical conditions, especially if the symptoms persist or are accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
**Q9: Can children have gooey stool, and is it treated differently?**
**A:** Yes, children can experience gooey stool. The causes and treatment approaches may differ slightly from adults. It’s important to consult with a pediatrician for evaluation and guidance.
**Q10: How can I prevent gooey stool from recurring?**
**A:** Preventing recurrent gooey stool involves identifying and addressing the underlying cause. This may include dietary modifications, stress management, probiotic supplementation, and addressing any underlying medical conditions.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Digestive Health
Gooey stool, while often unsettling, is a common digestive issue that can often be managed effectively. By understanding the potential causes, implementing appropriate dietary and lifestyle changes, and seeking medical attention when necessary, you can take control of your digestive health and improve your overall well-being. Remember, paying attention to your body’s signals and seeking expert advice are key to resolving this issue and maintaining a healthy gut. We hope this comprehensive guide has empowered you with the knowledge and insights you need to address your concerns about gooey stool.
Consider sharing your experiences with managing your digestive health in the comments below. If you are experiencing persistant digestive issues, consult with your healthcare provider to explore comprehensive solutions.