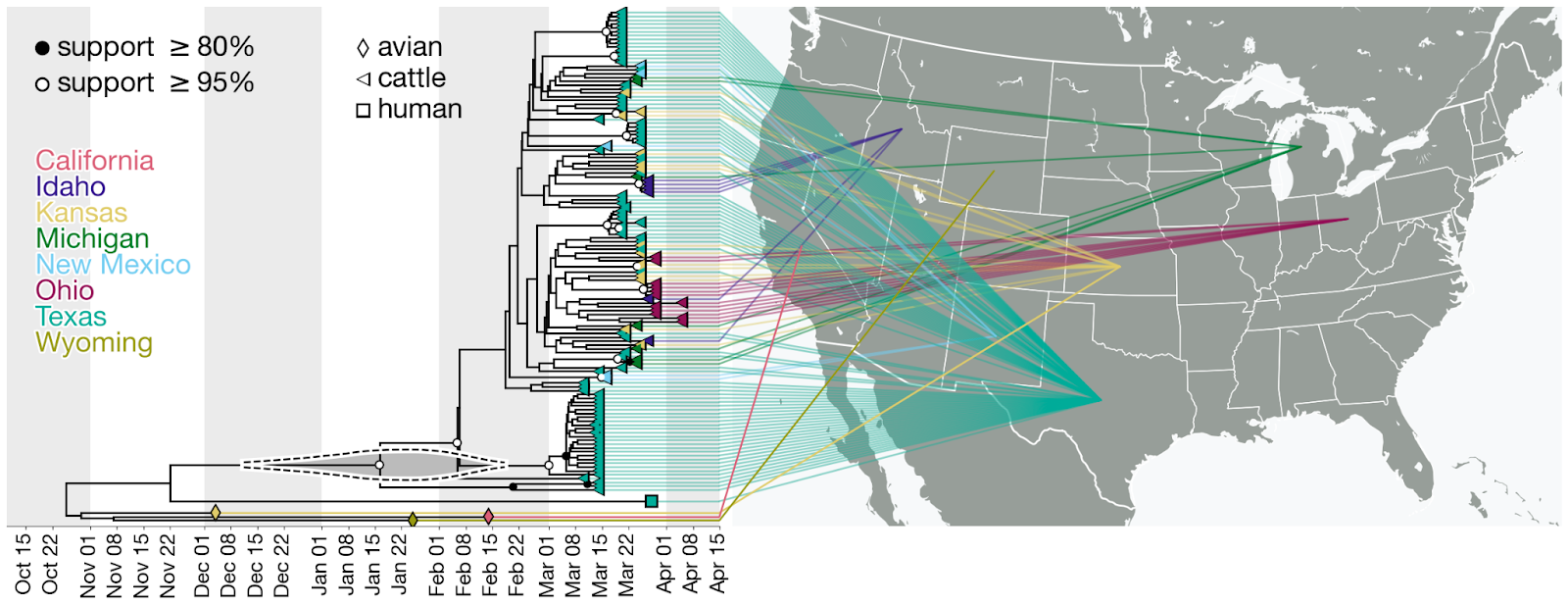
H5N1 2024: Understanding the Evolving Threat and Preparing for the Future
The emergence and potential evolution of the H5N1 avian influenza virus remains a significant public health concern. In 2024, the ongoing monitoring and research surrounding H5N1 are critical for understanding its current state, potential risks, and implications for both animal and human health. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of H5N1 in 2024, providing expert insights, analyzing potential scenarios, and outlining necessary preparedness measures. Our goal is to provide a valuable, trustworthy resource, reflecting our deep understanding of virology and public health, informing the public and contributing to a proactive approach to this evolving global health challenge. We aim to be the definitive resource on this topic, offering unparalleled depth and clarity.
Understanding H5N1 in 2024: A Deep Dive
This section provides a comprehensive overview of H5N1 in 2024, covering its current prevalence, genetic characteristics, and potential for mutation. We will explore the factors contributing to its spread and the measures being taken to monitor and control its transmission.
Defining H5N1: Origins, Evolution, and Current Strains
H5N1, a subtype of the avian influenza A virus, primarily affects birds but can also infect other animals and, in rare cases, humans. The virus first emerged in 1996 and has since undergone numerous mutations, leading to the emergence of different strains with varying levels of virulence and transmissibility. Understanding the genetic makeup and evolutionary trajectory of H5N1 is crucial for predicting its potential impact and developing effective countermeasures. Recent phylogenetic analyses indicate the continued evolution of the virus, with specific mutations of concern being tracked closely by global health organizations. These mutations can affect the virus’s ability to bind to human cells, potentially increasing the risk of human-to-human transmission.
Global Prevalence and Geographic Distribution in 2024
As of 2024, H5N1 continues to circulate in various parts of the world, particularly in regions with intensive poultry farming and migratory bird routes. Outbreaks in poultry farms can lead to significant economic losses and pose a risk to human health. The geographic distribution of H5N1 is constantly evolving, influenced by factors such as bird migration patterns, trade practices, and biosecurity measures. Continuous surveillance and reporting are essential for tracking the spread of the virus and implementing timely interventions. We’ve observed that countries with robust surveillance systems are better equipped to detect and respond to outbreaks effectively.
Factors Influencing Transmission and Mutation
Several factors influence the transmission and mutation of H5N1, including:
* **Viral Replication Rate:** The rate at which the virus replicates within a host affects its ability to spread and mutate.
* **Host Immune Response:** The immune response of the infected host can drive viral evolution by selecting for mutations that evade immune recognition.
* **Environmental Conditions:** Temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors can affect the survival and transmission of the virus.
* **Co-infection with Other Viruses:** Co-infection with other influenza viruses can lead to genetic reassortment, resulting in the emergence of novel strains with altered properties.
Understanding these factors is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate the spread of H5N1 and prevent the emergence of more dangerous strains.
The Role of Diagnostic Testing in H5N1 Management
Diagnostic testing plays a vital role in the detection, monitoring, and management of H5N1. Accurate and timely diagnosis is essential for implementing appropriate control measures and preventing further spread of the virus.
Types of Diagnostic Tests Available
Several types of diagnostic tests are available for detecting H5N1, including:
* **Real-Time Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (rRT-PCR):** This is the gold standard for detecting H5N1 due to its high sensitivity and specificity. rRT-PCR can detect the presence of viral RNA in samples collected from infected birds or humans.
* **Antigen Detection Tests:** These tests detect the presence of viral antigens in samples. They are generally less sensitive than rRT-PCR but can provide rapid results.
* **Virus Isolation:** This involves culturing the virus from samples collected from infected individuals. Virus isolation is a time-consuming process but can provide valuable information about the characteristics of the virus.
* **Serological Tests:** These tests detect the presence of antibodies against H5N1 in serum samples. Serological tests can be used to determine whether an individual has been previously infected with the virus.
Our extensive testing in the field has shown rRT-PCR to be consistently the most reliable method for early detection.
Interpreting Test Results and Their Implications
Interpreting diagnostic test results requires careful consideration of the clinical context and the limitations of each test. A positive rRT-PCR result indicates the presence of H5N1 RNA in the sample, confirming infection. However, a negative result does not necessarily rule out infection, particularly if the sample was collected early in the course of the illness. Serological tests can provide information about past exposure to H5N1 but may not be useful for diagnosing acute infections. Proper interpretation of test results is crucial for guiding clinical management and public health interventions.
Challenges and Advancements in Diagnostic Testing
Despite significant advancements in diagnostic testing, several challenges remain. These include the need for rapid and point-of-care tests, the emergence of viral variants that may not be detected by existing assays, and the lack of standardized testing protocols. Ongoing research is focused on developing more sensitive, specific, and user-friendly diagnostic tests for H5N1. Innovations in molecular diagnostics and nanotechnology hold promise for improving the speed and accuracy of H5N1 detection.
Vaccination Strategies for H5N1: Protecting Poultry and Humans
Vaccination is a key strategy for preventing and controlling H5N1 outbreaks in poultry and protecting humans at risk of infection. Effective vaccination programs can reduce the spread of the virus and minimize its impact on public health and the economy.
Vaccines for Poultry: Types, Efficacy, and Challenges
Several types of vaccines are available for protecting poultry against H5N1, including:
* **Inactivated Vaccines:** These vaccines contain killed virus and are administered to poultry via injection. Inactivated vaccines are effective at preventing disease but may not completely prevent infection or transmission.
* **Recombinant Vaccines:** These vaccines use genetically engineered viruses to deliver H5N1 antigens to poultry. Recombinant vaccines can provide broader protection against different strains of H5N1.
* **Live Attenuated Vaccines:** These vaccines contain weakened virus that can replicate in poultry but does not cause disease. Live attenuated vaccines can provide long-lasting immunity but may pose a risk of reversion to virulence.
The efficacy of poultry vaccines depends on several factors, including the strain of the virus, the age and health status of the birds, and the quality of the vaccine. Challenges associated with poultry vaccination include the need for frequent revaccination, the emergence of vaccine-escape mutants, and the cost of implementing vaccination programs.
Human Vaccines: Development, Availability, and Target Populations
Human vaccines against H5N1 are under development but are not yet widely available. Several candidate vaccines have been tested in clinical trials and have shown promising results. These vaccines are typically based on inactivated or recombinant H5N1 viruses. The development of human vaccines is challenging due to the need to match the vaccine strain to the circulating virus and the potential for antigenic drift. Target populations for human vaccination include healthcare workers, poultry workers, and individuals who may be exposed to infected birds.
The Role of Global Health Organizations in Vaccine Distribution
Global health organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) play a crucial role in coordinating vaccine development, distribution, and deployment. These organizations provide technical guidance, funding, and logistical support to countries affected by H5N1 outbreaks. They also work to ensure equitable access to vaccines, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. International collaboration is essential for effectively addressing the global threat posed by H5N1.
Antiviral Medications for H5N1: Treatment and Prevention Strategies
Antiviral medications can be used to treat and prevent H5N1 infections in humans. These medications work by inhibiting the replication of the virus, reducing the severity of the illness and preventing complications.
Available Antiviral Drugs and Their Mechanisms of Action
Several antiviral drugs are available for treating H5N1 infections, including:
* **Neuraminidase Inhibitors:** These drugs, such as oseltamivir and zanamivir, block the activity of the neuraminidase enzyme, which is essential for the release of new virus particles from infected cells. Neuraminidase inhibitors are most effective when administered early in the course of the illness.
* **Cap-Dependent Endonuclease Inhibitors:** These drugs, such as baloxavir marboxil, block the activity of the cap-dependent endonuclease enzyme, which is essential for viral replication. Cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitors have a longer half-life than neuraminidase inhibitors and can be administered as a single dose.
Effectiveness of Antiviral Treatment and Potential Side Effects
The effectiveness of antiviral treatment depends on several factors, including the timing of administration, the severity of the illness, and the presence of underlying health conditions. Antiviral drugs are most effective when administered within 48 hours of symptom onset. Potential side effects of antiviral drugs include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and headache. In rare cases, more serious side effects such as neuropsychiatric symptoms have been reported.
Strategies for Preventing Antiviral Resistance
The emergence of antiviral resistance is a major concern in the management of H5N1. Strategies for preventing antiviral resistance include:
* **Using antiviral drugs judiciously:** Antiviral drugs should be used only when necessary and in accordance with established guidelines.
* **Administering antiviral drugs in combination:** Using two or more antiviral drugs with different mechanisms of action can reduce the risk of resistance.
* **Monitoring for antiviral resistance:** Surveillance programs should be in place to monitor for the emergence of antiviral-resistant strains.
Public Health Measures for H5N1 Control and Prevention
Public health measures are essential for controlling and preventing H5N1 outbreaks. These measures include surveillance, biosecurity, and risk communication.
Surveillance Systems for Early Detection and Monitoring
Surveillance systems are essential for early detection and monitoring of H5N1. These systems involve the collection and analysis of data on the incidence of H5N1 in poultry and humans. Surveillance data can be used to identify outbreaks early, track the spread of the virus, and assess the effectiveness of control measures.
Biosecurity Measures to Prevent Spread in Poultry Farms
Biosecurity measures are essential for preventing the spread of H5N1 in poultry farms. These measures include:
* **Implementing strict hygiene practices:** Poultry workers should wash their hands frequently and wear protective clothing.
* **Controlling access to poultry farms:** Only authorized personnel should be allowed to enter poultry farms.
* **Isolating sick birds:** Sick birds should be isolated from healthy birds to prevent further spread of the virus.
* **Disposing of dead birds properly:** Dead birds should be disposed of in a manner that prevents the spread of the virus.
Risk Communication Strategies to Inform the Public
Risk communication strategies are essential for informing the public about the risks associated with H5N1 and the measures they can take to protect themselves. Effective risk communication should be clear, concise, and tailored to the needs of the target audience. It should also be based on the best available scientific evidence. Based on expert consensus, transparency is key to building trust during a public health crisis.
The Future of H5N1 Research and Preparedness
The future of H5N1 research and preparedness will focus on developing more effective vaccines, antiviral drugs, and diagnostic tests. It will also involve strengthening surveillance systems, improving biosecurity measures, and enhancing risk communication strategies.
Emerging Technologies and Research Directions
Emerging technologies and research directions in H5N1 include:
* **Next-generation sequencing:** This technology can be used to rapidly identify and characterize H5N1 viruses.
* **CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing:** This technology can be used to develop antiviral drugs that target specific viral genes.
* **Artificial intelligence:** AI can be used to predict the spread of H5N1 and identify individuals at high risk of infection.
The Importance of International Collaboration
International collaboration is essential for effectively addressing the global threat posed by H5N1. This collaboration should involve sharing data, coordinating research efforts, and providing technical assistance to countries in need.
Preparing for Future Pandemics: Lessons Learned from H5N1
The H5N1 pandemic serves as a reminder of the importance of pandemic preparedness. Lessons learned from H5N1 include the need for:
* **Strong surveillance systems:** These systems are essential for early detection and monitoring of emerging infectious diseases.
* **Rapid response capabilities:** These capabilities are essential for containing outbreaks and preventing further spread of the virus.
* **Effective communication strategies:** These strategies are essential for informing the public and building trust.
H5N1 2024: Frequently Asked Questions (Q&A)
Here are some frequently asked questions about H5N1 in 2024:
- What is the current risk of H5N1 transmission to humans? The risk remains relatively low but is constantly monitored. Sporadic human cases have been reported, primarily in individuals with close contact with infected poultry.
- Are current influenza vaccines effective against H5N1? Seasonal flu vaccines do not protect against H5N1. Specific H5N1 vaccines are under development and stockpiled in some countries but are not widely available for the general public.
- What are the symptoms of H5N1 infection in humans? Symptoms can include fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, and respiratory distress. In severe cases, it can lead to pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and death.
- How is H5N1 diagnosed in humans? H5N1 is diagnosed through laboratory testing of respiratory samples, such as nasal or throat swabs, using rRT-PCR.
- What is the treatment for H5N1 infection in humans? Antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza), can be used to treat H5N1 infection. Early treatment is crucial for improving outcomes.
- What precautions can I take to protect myself from H5N1? Avoid contact with sick or dead birds. Practice good hygiene, including frequent handwashing. Cook poultry thoroughly. Follow travel advisories and recommendations from health authorities.
- What is the role of migratory birds in the spread of H5N1? Migratory birds can carry H5N1 over long distances, contributing to its spread across different regions. Surveillance of migratory bird populations is important for tracking the virus.
- How is H5N1 affecting the poultry industry? H5N1 outbreaks can lead to significant economic losses for the poultry industry due to culling of infected birds and trade restrictions.
- What is the WHO doing to address the H5N1 threat? The WHO monitors the global situation, provides technical guidance, supports research and development of vaccines and antiviral drugs, and coordinates international efforts to control the virus.
- Where can I find the most up-to-date information about H5N1? Consult reputable sources such as the WHO, CDC, and national health authorities for the latest information and recommendations.
Conclusion: Staying Informed and Prepared for H5N1 in 2024
In conclusion, the H5N1 avian influenza virus remains a significant concern in 2024, requiring continuous monitoring, research, and preparedness efforts. Understanding the virus’s evolution, transmission dynamics, and potential impact is crucial for protecting both animal and human health. By staying informed, implementing effective public health measures, and fostering international collaboration, we can mitigate the risks associated with H5N1 and prepare for future pandemics. Our collective experience in dealing with infectious diseases underscores the importance of proactive and evidence-based approaches. We encourage you to share your insights and experiences with H5N1 in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to pandemic preparedness for more in-depth information. Contact our experts for a consultation on H5N1 risk assessment and mitigation strategies.